Child Development, Learning and Assessment
Test Objectives
- Understand early child development from birth to grade two and factors that affect development and learning.
- Understand the early childhood curriculum and how to plan instruction that is based on knowledge of young children from birth to grade two, their families and communities and curricular goals.
Question #1
Object permanence is a milestone of cognitive development that typically is fully functional in infants by what age?
You answered
Correct Answer: B
What is Object Permanence? Object Permanence is the understanding that whether something can be seen or sensed, it still continues to exist in the mind and in the world. Between the ages of 18-24 months most infants will have a fully functional sense of object permanence. Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget, studied object permanence in infants and determined it to be one of the most important accomplishments in infant development.
Peek-a-boo is a classic game that allows us to see if a child does in fact have object permanence. The child’s genuine surprise that an object or a person was hidden and then reappears is an indication that object permanence has not yet emerged.
The phrase that bests fits a child without Object Permanence is “out of sight, out of mind” while for the child with object permanence, “Out of sight, still exists” is a better fit. Once children begin to developed the concept that something no longer visible still exists in the world, evidence of separation anxiety begins to develop. Separation anxiety is usually at its peak between 10-18 months.
Question #2
Children need to experience the physical representation of numbers before they can understand the symbolic representation of number. This is according to the theory of
You answered
Best Response: D
Jean Piaget
This question aligns with the idea that young children need lots of hands-on experiences manipulating actual objects in order to construct an understanding of number concepts. Once children build and internalize number sense, they can more readily shift to thinking about numbers in more abstract ways (number symbols, mental math, etc.)
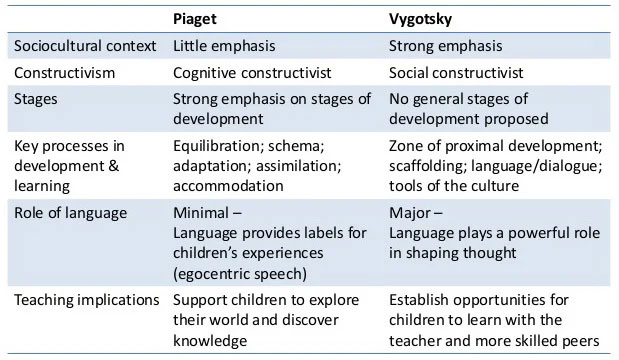
You will want to be aware of some key aspects of Piaget’s work around cognitive development and constructivism. Familiarize yourself with the terms: Schema, Assimilation and Accommodation, and Piaget’s stages of development: sensory-motor (0-2 years); pre-operational (2-7 years), concrete operational (7-11 years) and formal operational (11- adulthood)
Question #3
Which of the following scenarios in a kindergarten class would best support Lev Vygotsky's social constructivist theory of learning?
You answered
Correct Response: D.
According to Lev Vygotsky’s social constructivist theory of learning, social learning precedes development. Vygotsky noted that “Every function in the child’s cultural development appears twice: first, on the social level, and later, on the individual level; first, between people and then inside the child.” Additionally, he stated that often children will learn from a “More Knowledgeable Other”, as demonstrated in this scenario. One child learns a new puzzle-solving strategy by observing another child use the strategy first.
You’ll want to be aware of additional terms associated with Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory of learning such as: Scaffolding, Zone of Proximal Development, and Private/Inner Speech compared to social or external speech.
Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development suggests that intelligence changes as children grow. A child’s cognitive development is not just about acquiring knowledge, the child has to develop or construct a mental model of the world.
Learn more about Jean Piaget: https://www.simplypsychology.org/piaget.html
Lev Vygotsky believed that cognitive development was founded on social interaction. According to Vygotsky, much of what children acquire in their understanding of the world is the product of collaboration with others.
Learn more about Lev Vygotsky: https://www.simplypsychology.org/vygotsky.html
Question #4
In the typical course of infant development, which of the following developmental milestones is generally the latest to appear?
You answered
Correct Response: C.
Typical infant development follows a characteristic sequence of milestones as the infant brain and body mature. Of the milestones listed, smiling at familiar faces, turning the head to locate a sound, and making cooing sounds typically appear between 1-3 months of age, while the milestone of rolling over (either from stomach to back or back to stomach) is most often acquired between the ages of 4 and 7 months.
For this sub area of the content test, you will want to be aware of other key benchmarks in infant and child development. Click on these links to review/download the Brightstart resource Developmental Milestones Birth-Age 3 and the Cleveland Clinic’s Motor Skill Development Charts.
Question #5
Which behavior indicates a child has attained an understanding of symbolic representation?
You answered
Correct Answer: B
When children engage in pretend or “make-believe” play, as when they play “house” and pretend to be parents; pretend to be fantasy characters; or use toys to represent real persons, animals or machines, etc. they understand that one thing can be used as a symbol to stand for something else. This is what is called Symbolic Representation.

The symbolic nature of play moves from less to more advanced. These images offer a great visual for how the hypothetical and imaginary worlds of children’s play can move along a continuum from more concrete symbolism (toy phone) to abstract symbolism (banana as a phone or completely improvised phone). As children move from the concrete to the abstract, their thinking becomes more and more imaginative and creative.
Question #6
Four 3-year-old boys and girls are playing with dolls on the floor. Each child is holding and grooming one doll without interacting with a nearby neighbor. Which of the following categories of play does this scenario describe?
You answered
Correct Answer: C
The question requires applying knowledge of play modes for young children. It describes a state of parallel play, in which children are playing separately from others but with similar toys or in a manner that mimics their neighbor’s play.
Question #7
Ms. Johnson’s class of kindergarteners are learning to use visual information as a way to convey their ideas. Which is an ideal literacy activity she might integrate into a science unit on bugs?
You answered
Correct Answer: D
Having children create a picture book of different bugs helps them understand how the visual representation of bugs in their book can convey information. It is also an ideal way to integrate science content and literacy goals.
Integrated curriculum offers learning experiences that cross the boundaries of traditional subject areas and are designed to be mutually reinforcing for the learner. This approach develops the child’s ability to transfer their learning to other settings.

Question #8
A second-grade teacher can promote students' creativity most effectively by adopting which of the following approaches?
You answered
Correct Response: B
Creative thinkers apply their knowledge and experience in original ways to make discoveries and expand their understanding. By encouraging second graders to problem solve on their own and come up with unusual solutions to a variety of challenges presented to them, the teacher is helping them become independent thinkers who respond to new experiences with imagination.
Question #9
A prekindergarten teacher is teaching a unit on the five senses. The teacher is planning a lesson about texture. Which of the following initial strategies is likely to be most effective in helping children construct meaning with regard to this concept?
You answered
Correct Response: C
Prekindergarten children are concrete learners who require direct experience with concrete objects to construct knowledge effectively. The opportunity to explore a concept with real materials and verbalize observations helps extend the depth of children’s understanding and promotes development of a meaningful vocabulary with regard to the targeted concept.
Question #10
A preschool child brings two toy boats to school to show at circle time. The child explains that the boats really float and the teacher invites the child to demonstrate in the water center. Another child states, "They float because they're small." A third child responds, "Big things can float, too." Soon all of the children begin discussing their ideas about what will and will not float. The teacher can best help children gain a better understanding of the concept of flotation by taking which of the following actions?
You answered
Correct Response: C
Preschool-age children learn best through direct physical interaction with concrete materials. In the situation described, the teacher applies knowledge of the way children learn by providing them with objects to use to test their ideas. Having the opportunity to place various objects on the surface of the water and observe and discuss the results will build the children’s understanding of what types of objects float and what types sink.
Question #11
The family and teachers of nine-month old Luisa, who attends and infant and toddler center, have become concerned that Luisa may have developmental delays. As a result, Luisa will soon undergo a series of developmental screening assessments. The primary purpose of these assessments should be to:
You answered
Correct Response: D
A Developmental Screening is a brief assessment that can be administered by early childhood teachers to help identify if a child is on track with their early childhood developmental milestones. Such screenings can help identify children who may be at risk for delays in cognitive, motor, communication, or social-emotional development. Such delays can affect a child’s learning, growth, and development, and may require further evaluation and intervention.
Often what follows such screenings for infants and toddlers is a referral for early intervention services offered through The Illinois Department of Human Services. Families are directed to their local Child and Family Connection Office where an early intervention coordinator would help develop an individualized plan to the meets of the child and family.
Find out more about this process here: https://youtu.be/JEQeCz55Hn4?si=jFGATDrshQGNpsiM
Question #12
Which of the following informal assessment tools would be most useful for documenting a preschool child's ability to perform specific skills?
You answered
Correct Response B.
This question requires the examinee to recognize informal assessments and their applications in early childhood programs. Although more subjective than various other assessments, a rating scale is a quick, efficient way to gather information without disrupting learning.
Using a rating scale over time would allow the teacher to monitor and document a child’s performance of specific skills and to provide timely intervention as necessary.
Unlike using a simple checklist assessment, a Rating Scale allows the observer to rate the quality, frequency or ease with which a child uses a certain skill.
Read NAEYC’s Statement on Observing, Documenting and Assessing Young Children

Question #13
A teacher is planning to conduct an informal assessment of a first grader's reading fluency. In the assessment, the teacher will ask the child to read aloud a passage from a grade-level text for one minute. Which of the following criteria would be appropriate for the teacher to apply in the context of this assessment?
You answered
Correct Response: D.
Fluent readers employ prosody (e.g., pitch, stress, timing) to interpret and convey the meaning of the text they are reading. A child who reads an author’s words with appropriate phrasing and expression is demonstrating key indicators associated with reading fluency.
Question #14
A kindergarten teacher wants to obtain general information about a child's development in several areas of emergent literacy. Which of the following informal assessments would be most effective in providing information across several areas of emergent literacy?
You answered
Correct Response: C.
Asking a kindergartner to write a title on a picture he or she has just drawn would provide the teacher with a variety of information. For example, this task would show whether the child understands that writing is different from drawing and that print is directional. It would demonstrate the child’s letter-formation skills. It would also be likely to provide information on the child’s understanding of letter-sound correspondence (e.g., if the child uses letters and words that correspond to the names of the objects in the drawing).
Question #15
A three year old and a four year old have been competing for opportunities to ride the swing. Both children are capable of seating themselves in the swing and pushing it. Which of the following responses from their preschool teacher will best serve to foster the children’s social problem solving skills?
You answered
Correct Response: B
Rather than taking the lead in identifying the issue causing the conflict and determining best way to resolve it, the teacher can reinforce problem solving strategies and communication skills by asking the children to describe the problem as they perceive it then encourage the children to come up with viable solutions that they can both agree upon. When children take an active role in finding solutions to such conflicts, they will be more motivated to accept and apply the new resolution.
Question #16
A first-grade teacher establishes and teaches students specific routines for times such as morning arrival, weekly class meetings, and daily silent reading. This practice can be expected to support students' learning and development primarily by:
You answered
Correct Response: A
Classroom routines create predictability in the learning environment and help children understand expectations and boundaries. When children know what to expect and how to perform various tasks and responsibilities, they gain confidence and security and tend to be less distracted and anxious. Routines allow children to focus more of their attention on the important task of learning.
Question #17
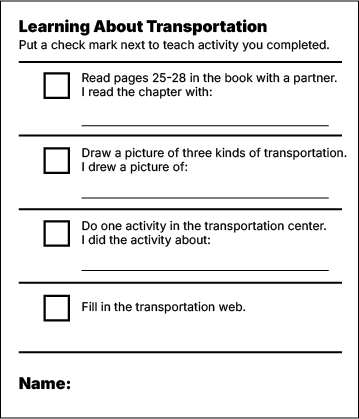
Students in a second-grade class are studying transportation. During this unit, the teacher provides students with a checklist (view checklist). Every day or two, the teacher reviews each child's checklist and guides the children in keeping their checklists up to date. This strategy is likely to be especially effective for helping the students:
You answered
Correct Response: B
One of an early childhood teacher’s key responsibilities is to promote young children’s growth as independent learners. By routinely providing children with opportunities to work with partners, make independent choices, and monitor their own activities, the teacher encourages children to assume responsibility for their own learning. Providing children with such opportunities on a regular basis promotes children’s development of independent habits of mind.
Question #18
Which of the following would be a second-grade teacher's best strategy for promoting all students' sense of competence and motivation to learn?
You answered
Correct Response: B
This question requires the examinee to apply knowledge of supportive learning environments that promote students’ sense of competence and motivation to learn. Research has shown that children are motivated by high but realistic learning expectations.
Differentiating instruction allows teachers to set learning expectations at the appropriate level for each student. Students who believe that they can achieve success through effort and persistence become self-confident, motivated learners.
Question #19
Jamie, a child with Down syndrome, will soon join a general education kindergarten class. When doing educational planning for this child, the kindergarten teacher should be aware that the typical developmental profile for children with Down syndrome includes relative strength in which of the following areas?
You answered
Correct Response: A.
The typical learning profile of children with Down syndrome includes strength in visual processing and visual memory skills. Jamie’s general education teacher should work closely with the special education teacher to determine whether this is the case with Jamie and, depending on Jamie’s specific learning profile, to develop instructional strategies that build on the learning strengths Jamie brings to the classroom.
