Understand early child development from birth to grade two and factors that affect development and learning.
Test Objectives
Please note: An option must be selected in order to flip the card to see the correct answer and/or supplemental information.
Question #1
Object permanence is a milestone of cognitive development that typically is fully functional in infants by what age?
You answered
Correct response: B
What is Object Permanence? Object Permanence is the understanding that whether something can be seen or sensed, it still continues to exist in the mind and in the world. Between the ages of 18-24 months most infants will have a fully functional sense of object permanence. Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget, studied object permanence in infants and determined it to be one of the most important accomplishments in infant development.
Peek-a-boo is a classic game that allows us to see if a child does in fact have object permanence. The child’s genuine surprise that an object or a person was hidden and then reappears is an indication that object permanence has not yet emerged.
The phrase that bests fits a child without Object Permanence is “out of sight, out of mind” while for the child with object permanence, “Out of sight, still exists” is a better fit. Once children begin to develop the concept that something no longer visible still exists in the world, evidence of separation anxiety begins to develop. Separation anxiety is usually at its peak between 10-18 months.
Question #2
Children need to experience the physical representation of numbers before they can understand the symbolic representation of number. This is according to the theory of
You answered
Correct response: D
Jean Piaget
This question aligns with the idea that young children need lots of hands-on experiences manipulating actual objects in order to construct an understanding of number concepts. Once children build and internalize number sense, they can more readily shift to thinking about numbers in more abstract ways (number symbols, mental math, etc.)
You will want to be aware of some key aspects of Piaget’s work around cognitive development and constructivism. Familiarize yourself with the terms: Schema, Assimilation and Accommodation, and Piaget’s stages of development: sensory-motor (0-2 years); pre-operational (2-7 years), concrete operational (7-11 years) and formal operational (11- adulthood)
Question #3
Which of the following scenarios in a kindergarten class would best support Lev Vygotsky's social constructivist theory of learning?
You answered
Correct response: D
According to Lev Vygotsky’s social constructivist theory of learning, social learning precedes development. Vygotsky noted that “Every function in the child’s cultural development appears twice: first, on the social level, and later, on the individual level; first, between people and then inside the child.” Additionally, he stated that often children will learn from a “More Knowledgeable Other”, as demonstrated in this scenario. One child learns a new puzzle-solving strategy by observing another child use the strategy first.
You’ll want to be aware of additional terms associated with Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory of learning such as: Scaffolding, Zone of Proximal Development, and Private/Inner Speech compared to social or external speech.
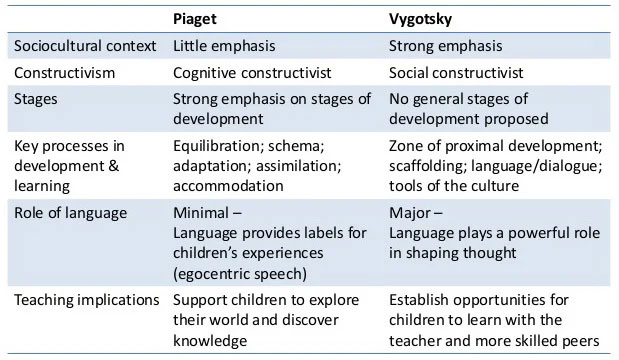
Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development suggests that intelligence changes as children grow. A child’s cognitive development is not just about acquiring knowledge, the child has to develop or construct a mental model of the world.
Learn more about Jean Piaget: https://www.simplypsychology.org/piaget.html
Lev Vygotsky believed that cognitive development was founded on social interaction. According to Vygotsky, much of what children acquire in their understanding of the world is the product of collaboration with others.
Learn more about Lev Vygotsky: https://www.simplypsychology.org/vygotsky.html
Question #4
Which behavior indicates a child has attained an understanding of symbolic representation?
You answered
Correct response: B
When children engage in pretend or “make-believe” play, as when they play “house” and pretend to be parents; pretend to be fantasy characters; or use toys to represent real persons, animals or machines, etc. they understand that one thing can be used as a symbol to stand for something else. This is what is called Symbolic Representation.
The symbolic nature of play moves from less to more advanced. These images offer a great visual for how the hypothetical and imaginary worlds of children’s play can move along a continuum from more concrete symbolism (toy phone) to abstract symbolism (banana as a phone or completely improvised phone). As children move from the concrete to the abstract, their thinking becomes more and more imaginative and creative.

Question #5
Four 3-year-old boys and girls are playing with dolls on the floor. Each child is holding and grooming one doll without interacting with a nearby neighbor. Which of the following categories of play does this scenario describe?
You answered
Correct response: C
The question requires applying knowledge of play modes for young children. It describes a state of parallel play, in which children are playing separately from others but with similar toys or in a manner that mimics their neighbor’s play.
Question #6
An English Language Learner (ELL) in the early production stage of second language acquisition joins a kindergarten class. The teacher can best ensure this student understands and is able to follow the teacher’s instruction by:
You answered
Correct response: A
Correct Response: A
There are many strategies teachers can use to support ELLs as they build both receptive and expressive English language skills in the classroom. Using gestures and visual cues, as well as using simple words or words with shared cognates (words in two languages that share a similar meaning, spelling and pronunciation such as the Spanish word información and the English word information)
For Sub Area 2 of the Early Childhood Content Test, you’ll want to be aware of The 5 Stages of Second Language Acquisition and their key characteristics. Click here for a graphic that will offer an overview and a link to video resources on this topic.
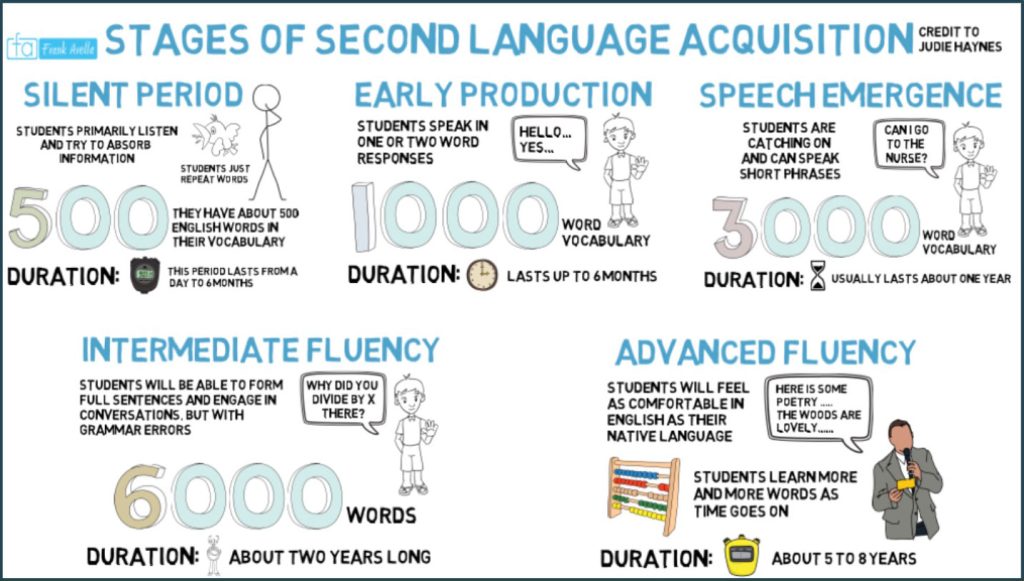
For more information, check out Teachings in Education’s Stages of Second Language Acquisition: ESL, ELL, LEP & Bilingual on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hk7_lBaFC5w
Question #7
In the typical course of infant development, which of the following developmental milestones is generally the latest to appear?
You answered
Correct response: C
Typical infant development follows a characteristic sequence of milestones as the infant brain and body mature. Of the milestones listed, smiling at familiar faces, turning the head to locate a sound, and making cooing sounds typically appear between 1-3 months of age, while the milestone of rolling over (either from stomach to back or back to stomach) is most often acquired between the ages of 4 and 7 months.
Be aware of other key benchmarks in infant and child development. Click on these links to review/download the Brightstart resource Developmental Milestones Birth-Age 3 and the Cleveland Clinic’s Motor Skill Development Charts.
