Understand word-identification strategies and vocabulary development and how to use evidence-based, developmentally appropriate strategies to promote word identification and vocabulary skills in young children from birth to grade two.
Test Objectives
Please note: An option must be selected in order to flip the card to see the correct answer and/or supplemental information.
Question #1
A kindergarten teacher conducts a literacy activity with a small group of students. The teacher gives each student a piece of paper with three connected boxes drawn on it. Each box represents a phoneme in a three-letter word. The teacher says a word slowly, pronouncing each phoneme distinctly. As the students hear each phoneme, they move a marker into the corresponding box. This activity provides the students with practice in:
You answered
Correct response: B
Sound segmentation activities require students to isolate each constituent sound in a word. Moving each marker into its own box to represent each sound encourages the students to associate one marker with one sound, thus laying a conceptual foundation for students’ later association of individual letters with their sounds.
This scenario refers to the use of a teaching tool called Elkonin Sound Boxes. They support young or struggling readers to develop phonemic awareness skills by helping them to better hear and manipulate the smallest units of sound in words.
This scenario refers to the use of a teaching tool called Elkonin Sound Boxes. They support young or struggling readers to develop phonemic awareness skills by helping them to better hear and manipulate phonemes, the smallest units of sound in words.

Learn more about this strategy here: https://www.understood.org/en/articles/evidence-based-literacy-strategy-elkonin-sound-boxes
Question #2
Phonological Awareness refers to the progressive range of skills that allow us to recognize and manipulate the sounds in spoken language. Which of the following skills represents the most complex level of phonological awareness?
You answered
Correct response: C
Segmenting individual sounds in words
Children’s phonological awareness skills follow a continuum of complexity. The most advanced level of phonological awareness is phonemic awareness. Phonemic awareness is the understanding that words are made up of individual sounds, or phonemes, and the ability to manipulate those phonemes either by segmenting, blending, or changing individual phonemes within words to create new words.
TIP: Be familiar with these 5 Levels of Phonological Awareness
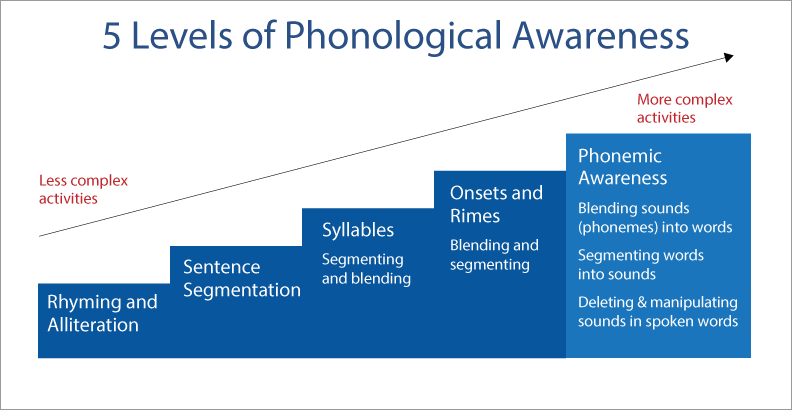
Graphic Source: https://blogs.sd41.bc.ca/slp/topic/early-literacy/phonological-awareness/
Phonemic Awareness Strategies and Terms
When the child struggles to decode a word and is told to “sound it out”, this strategy is guiding the child to use phoneme segmentation. Example: /B/ /A/ /T/
When a child can see and say the sounds of individual letters in a word and are then guided to blend them together, that is sound or phoneme blending. Example: B A T
When the teacher asks a child to replace the /B/ in BAT with the /M/ sound, this is called phoneme substitution. /B/ /A/ /T/ becomes /M/ /A/ /T/
When the teacher asks the child to take away the /B/ sound in BAT then what do you get? That is called phoneme deletion.
When exploring onset and rime, the teacher helps a child hear the changes in the initial consonant sounds of words that share the same rime or the vowels and consonants that come after the onset. Example: /b/at, /m/at, /c/at, /r/at, /th/at, /spl/at (these are also called phonograms or word families)
Question #3
A kindergarten teacher sets up a literacy center with an activity that asks students to match pictures of objects with pictures of letters to correctly indicate the beginning sound. Which of the following is the teacher trying to develop in students through this center?
You answered
Correct response: D
Phonemic Awareness skills are necessary for matching words or pictures with beginning sounds.
Option A (phonics) is incorrect because it involves understanding how letters combined to make sounds and words. Students are ready for phonics instruction after they have acquired a strong foundation of phonemic awareness.
Option B (Vocabulary), involves building children’s receptive and expressive vocabulary or word knowledge, which is not the goal of this activity.
Option C (letter recognition) is incorrect because this activity is not focused primarily on children identifying letters.
Question #4
A second-grade teacher is teaching a vocabulary lesson that focuses on the similarities, differences, and uses of the words to, two and too. This lesson is helping children learn about:
You answered
Correct response: B
Homophones are words that sound the same but are spelled differently, such as to, two, and too.
Related Terms to Know:
Homographs, by comparison, are words that are “graphically” spelled the same but have different meanings and may also be pronounced differently. Words such as bow, tie, and watch. Homographs require the reader to use context clues in order to make meaning of the word. For example: The knight was expected to bow before the Queen vs. The girl wore her favorite purple bow.
Synonyms are words that mean the same thing (i.e.: angry and furious; to collect and to gather)
Antonyms are words that hold opposite meanings (i.e.: left vs right, dark vs. light)